OSHA Compliance for Dental Offices
OSHA compliance is crucial for dental offices to ensure a safe working environment and protect employees from occupational hazards. It involves adhering to standards like bloodborne pathogen exposure control, proper waste disposal, and emergency preparedness. Dental offices must maintain accurate records of injuries and provide annual training to staff. Non-compliance can result in fines and legal consequences, making regular inspections and audits essential to maintain adherence to OSHA regulations.
1.1 Importance of OSHA Compliance in Dental Settings
OSHA compliance is essential for safeguarding dental office employees and patients from potential hazards. It ensures adherence to legal standards, preventing injuries and illnesses. Non-compliance can lead to fines and legal consequences. Proper training and safety protocols build a culture of safety, fostering trust and professionalism. Regular inspections and audits help maintain compliance, protecting both staff and patients while avoiding financial penalties and reputational damage.
1.2 Overview of OSHA Standards Relevant to Dental Offices
OSHA standards for dental offices include bloodborne pathogen exposure control, hazard communication, emergency preparedness, and recordkeeping. They require proper use of personal protective equipment, safe handling of hazardous materials, and annual employee training. Regular workplace inspections and reporting of work-related injuries are also mandated. Compliance ensures a safe environment, protects employees, and avoids legal penalties, making it essential for dental practices to adhere strictly to these regulations.

Bloodborne Pathogen Standards
Bloodborne pathogen standards are critical in dental offices to prevent exposure to infectious diseases. They require exposure control plans, use of PPE, and proper hygiene practices.
2.1 Understanding Bloodborne Pathogens in Dental Practice
Bloodborne pathogens, such as HIV and hepatitis, pose significant risks in dental settings due to exposure to blood and bodily fluids. Dental staff must recognize these hazards to implement appropriate precautions. Understanding the nature of bloodborne pathogens is essential for developing effective strategies to minimize exposure and protect both patients and employees. This knowledge forms the foundation of a safe dental practice environment.
2.2 Requirements for Exposure Control Plans
Dental offices must develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) to minimize bloodborne pathogen risks. The plan should identify exposure-prone tasks, outline engineering controls, and specify PPE requirements. Annual training and updates are mandatory. The ECP must also include procedures for handling needlestick injuries and post-exposure protocols. Regular reviews ensure compliance with OSHA standards, safeguarding both staff and patient health effectively.

Hazard Communication in Dental Offices
Hazard communication ensures dental staff safely handles chemicals. It involves labeling, SDS management, and training on potential risks, fostering a safer workplace environment for all employees.
3.1 Implementing a Hazard Communication Program
Implementing a hazard communication program in dental offices ensures staff safety by identifying chemical hazards. This involves labeling chemicals, maintaining Safety Data Sheets (SDS), and training employees on handling, storage, and emergency procedures. Clear communication of risks through SDS and proper labeling is essential. Regular updates and staff training ensure compliance with OSHA standards, promoting a safe workplace environment and preventing accidents related to chemical exposure.
3.2 Managing Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
Managing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) is critical for hazard communication in dental offices. SDS must be maintained, easily accessible, and updated regularly. They provide detailed information on chemical hazards, handling, and emergency procedures. Dental offices should organize SDS by product or alphabetically and ensure they are available to all employees; Regular reviews and updates of SDS are required to comply with OSHA standards and ensure workplace safety.

Emergency Preparedness and Response
Emergency preparedness is vital for dental offices to ensure staff and patient safety during crises. Develop a comprehensive emergency action plan, conduct drills, and maintain fire safety measures.
4.1 Developing an Emergency Action Plan
A comprehensive emergency action plan is essential for dental offices to respond effectively to crises like fires, natural disasters, or medical emergencies. The plan should outline evacuation routes, emergency contact details, and staff roles. Regular drills ensure preparedness, and coordination with local authorities enhances response efficiency. Tailor the plan to the office’s specific needs, ensuring all employees understand their responsibilities and safety protocols.
4.2 Fire Safety and Prevention Measures
Fire safety is critical in dental offices to protect staff and patients. Ensure proper storage of flammable materials and maintain clear evacuation routes. Install smoke detectors and fire extinguishers, ensuring they are inspected regularly. Conduct regular fire drills to train staff on emergency procedures. Keep emergency exit routes unobstructed and ensure all employees understand fire prevention measures and evacuation protocols in case of an emergency.

Recordkeeping Requirements
OSHA requires dental offices to maintain accurate records of work-related injuries and illnesses using the OSHA 300 Log. Employers must report incidents within specific timeframes.
5.1 Maintaining OSHA Records (300 Log)
Dental offices must maintain the OSHA 300 Log to record work-related injuries and illnesses accurately. Employers are responsible for updating the log promptly when incidents occur. The log must include details such as the nature of the injury, the affected employee, and the circumstances surrounding the incident. Accurate recordkeeping is essential for compliance and helps identify workplace safety trends. OSHA may request the log during inspections or audits.
5.2 Reporting Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses
Dental offices must report work-related injuries and illnesses to OSHA within specific timeframes, especially if they result in hospitalization or amputation. Employers are required to notify OSHA within 24 hours for inpatient hospitalizations and 8 hours for fatalities. Accurate reporting ensures compliance with OSHA standards and helps prevent future incidents. Failure to report can lead to penalties. OSHA may request additional details during inspections or audits.

Training Requirements for Dental Staff
Dental staff must receive annual OSHA training, covering topics like bloodborne pathogens, hazard communication, and emergency procedures. Training ensures compliance and prepares employees to handle workplace hazards effectively.
6.1 Annual OSHA Training Mandates
Annual OSHA training is mandatory for all dental staff at risk of occupational exposure. This training covers essential topics such as bloodborne pathogen standards, hazard communication, and emergency preparedness. It ensures employees are informed about workplace hazards and understand protective measures. Compliance with these mandates is critical to maintaining a safe environment and avoiding legal penalties. Regular updates keep staff informed of new regulations and best practices.
6.2 Topics to Cover in Dental Office Safety Training
Dental office safety training must cover essential topics such as bloodborne pathogen exposure control, hazard communication, and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Employees should also be trained on emergency procedures, fire safety, and waste management protocols. Infection control practices, sterilization techniques, and proper recordkeeping are additional key areas. Understanding these topics ensures compliance with OSHA standards and promotes a safe working environment for all staff members.
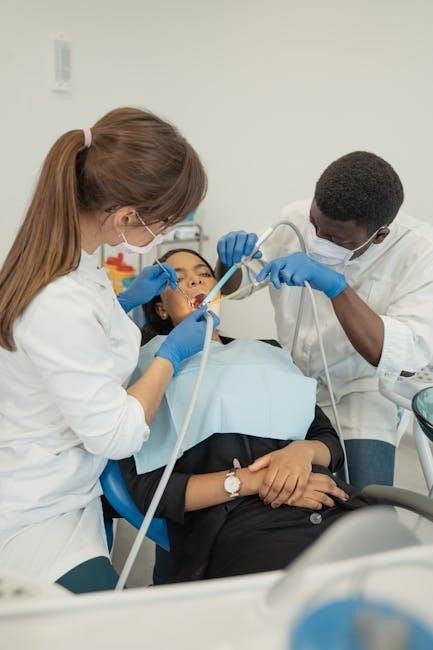
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential for dental staff to prevent exposure to bloodborne pathogens and chemicals. Gloves, masks, eye protection, and gowns are critical for safety.
7.1 Selection and Use of PPE in Dental Settings
Proper selection and use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in dental settings are critical to prevent exposure to bloodborne pathogens and chemicals. Gloves, masks, eye protection, and gowns are essential for procedures involving bodily fluids. Selection should align with the type of procedure and potential exposure risks. Ensure proper fit, donning, and doffing to maintain effectiveness. Regular training on PPE use is required for compliance with CDC and OSHA guidelines.
7.2 Proper Donning and Doffing Techniques
Proper donning and doffing of PPE are essential to prevent contamination and exposure to pathogens. Start with gloves, then masks, eye protection, and gowns. Remove PPE in reverse order, avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces. Use hand hygiene after removal. Training on correct techniques ensures compliance with OSHA and CDC guidelines, minimizing cross-contamination risks and protecting both staff and patients.

Waste Management and Disposal
Proper waste management in dental offices is critical for safety and compliance. It involves segregating biohazardous, chemical, and general waste, ensuring disposal adheres to OSHA and environmental regulations.
8.1 Biohazardous Waste Disposal Guidelines
Biohazardous waste disposal in dental offices requires strict adherence to OSHA standards. Waste must be segregated into designated containers, properly labeled, and treated, often via autoclave, before disposal. Dental offices must use puncture-proof containers for sharps and ensure biohazardous waste is disposed of through licensed facilities. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations is essential to prevent environmental contamination and ensure staff safety.
8.2 Proper Handling of Chemical Waste
Proper handling of chemical waste in dental offices involves segregating materials by type, using compatible containers, and ensuring proper labeling. Staff must follow Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for disposal instructions. Chemical waste should be stored in designated areas away from incompatible substances. Disposal must comply with local, state, and federal regulations, often requiring licensed facilities. Training on chemical handling and spill cleanup is essential to minimize risks and ensure compliance with safety standards.

Patient Safety and Infection Control
Patient safety and infection control are critical in dental settings to prevent disease transmission. Proper infection control practices, sterilization protocols, and use of PPE are essential. Adherence to OSHA and CDC guidelines ensures a safe environment for both patients and staff, minimizing risks associated with infectious agents in dental care.
9.1 Infection Control Practices in Dentistry
Infection control practices in dentistry are essential to prevent the transmission of infectious agents. These practices include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and proper disinfection of surfaces and instruments. Dental offices must adhere to OSHA and CDC guidelines to ensure a safe environment for both patients and staff. Proper protocols help minimize the risk of exposure to pathogens during dental procedures. Regular training and compliance with these standards are critical to maintaining infection control. Adherence to these practices also protects patients from potential infections, ensuring a safe and healthy care environment. By following these guidelines, dental offices can effectively reduce the risk of infection transmission and maintain high standards of patient safety.
9.2 Sterilization and Disinfection Protocols
Sterilization and disinfection protocols are critical in dental offices to eliminate pathogens from instruments and surfaces. Autoclaving is the most effective method for sterilizing dental instruments, while disinfectants are used for non-invasive equipment. Proper protocols must follow CDC and OSHA guidelines to ensure all surfaces and tools are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected between patients. This helps prevent cross-contamination and maintains a safe environment for both patients and staff. Adherence to these protocols is essential for compliance with infection control standards and ensuring patient safety. Regular monitoring and training on sterilization procedures are necessary to maintain consistency and effectiveness in infection control practices.

Regular Inspections and Audits
Regular inspections and audits are essential for maintaining safety and compliance in dental offices, identifying hazards, and ensuring adherence to OSHA standards through consistent evaluations and improvements;
10.1 Conducting Regular Workplace Inspections
Regular workplace inspections are vital for identifying and addressing potential hazards in dental offices. These inspections should be thorough, covering areas like equipment, storage, and infection control practices. Dental offices must document findings, implement corrective actions, and involve staff to foster a culture of safety. Consistent inspections help prevent accidents and ensure ongoing compliance with OSHA standards, safeguarding both employees and patients.
10.2 Preparing for OSHA Inspections
Preparing for OSHA inspections involves organizing records, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and training staff. Dental offices should maintain updated OSHA logs, safety data sheets, and emergency plans. Conduct mock inspections to identify gaps and address them promptly. Ensuring all equipment is properly labeled and staff are knowledgeable about protocols helps demonstrate compliance. A well-prepared office can efficiently manage an OSHA inspection, minimizing potential violations and penalties.
